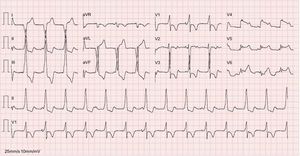
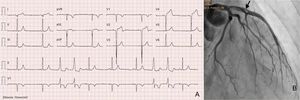
The second and seventh complexes (Figure 1) could lead to misdiagnosis of a left lateral accessory pathway but the absence of pre-excitation in the remaining complexes clearly excludes that diagnosis (answer 1, incorrect).1,2 The atrioventricular (AV) dissociation during accelerated idioventricular rhythm is an isorhythmic AV dissociation with ventricular rate similar to or faster than atrial rate (answer 2, correct), where the AV dissociation is not isorhythmic with atrial rate much faster than ventricular rate (answer 3, incorrect). A second ECG (Figure 2A) performed 2minutes after the first ECG revealed sinus rhythm, ventricular extrasystoles with the same focus as the first ECG and pathological q waves in V1-V4; DI and aVL leads, and no ST-segment elevation in V5-V6, probably showing an already evolutionary phase of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (answer 4, incorrect). An emergent coronary angiogram revealed the presence of a thrombus (arrow) in the left anterior descending artery (Figure 2B).
ISSN: 1885-5857
Impact factor 2023
7.2