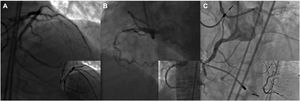
Coronary chronic total occlusions (CTO) involving bifurcation lesions are a challenging lesion subset that is understudied in the literature. This study analyzed the incidence, procedural strategy, in-hospital outcomes and complications of percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) for bifurcation-CTO (BIF-CTO).
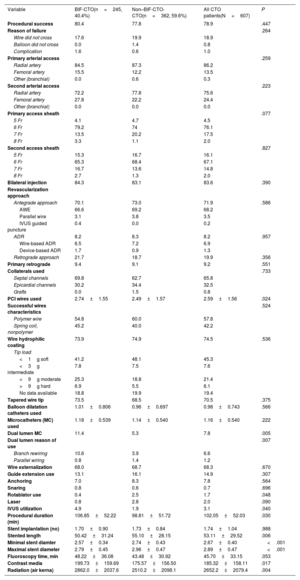
MethodsWe assessed data from 607 consecutive CTO patients treated at the Institut Cardiovasculaire Paris Sud (ICPS), Massy, France between January 2015 and February 2020. Procedural strategy, in-hospital outcomes and complication rates were compared between 2 patient subgroups: BIF-CTO (n=245=and non–BIF-CTO (n=362).
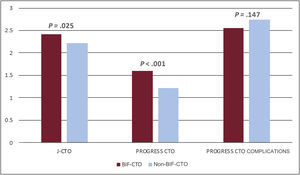
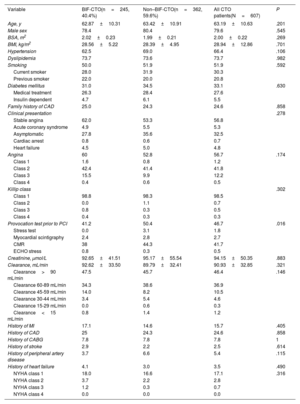
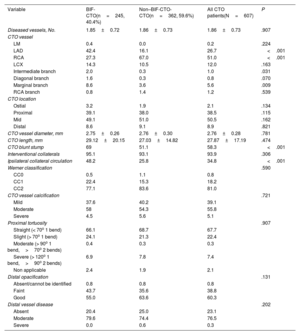
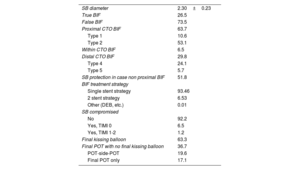
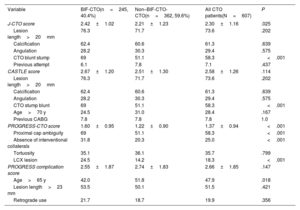
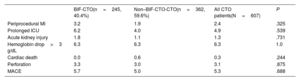
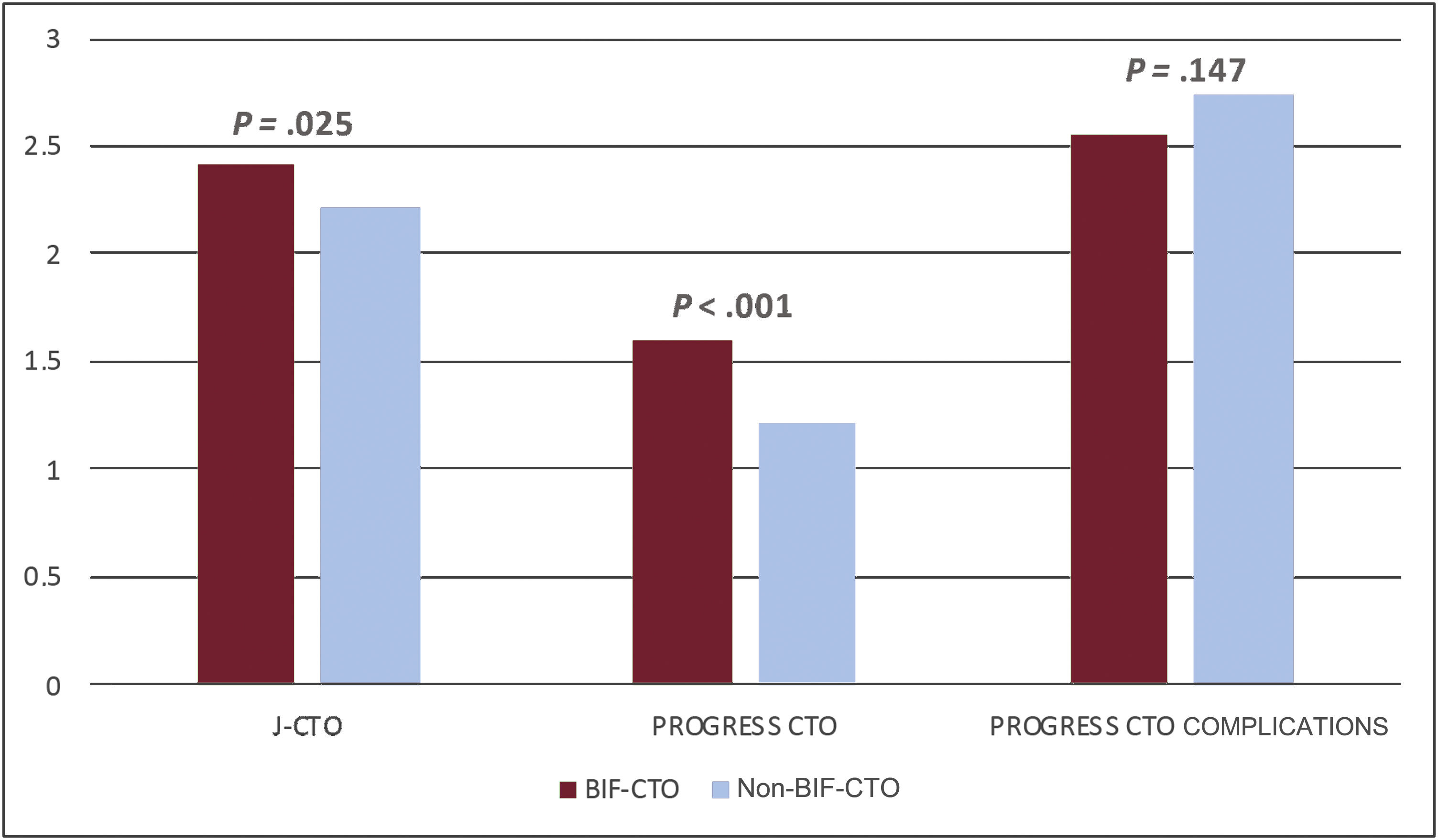
ResultsThe mean patient age was 63.2±10.6 years; 79.6% were men. Bifurcation lesions were involved in 40.4% of the procedures. Overall lesion complexity was high (mean J-CTO score 2.30±1.16, mean PROGRESS-CTO score 1.37±0.94). The preferred bifurcation treatment strategy was a provisional approach (93.5%). BIF-CTO patients presented with higher lesion complexity, as assessed by J-CTO score (2.42±1.02 vs 2.21±1.23 in the non–BIF-CTO patients, P=.025) and PROGRESS-CTO score (1.60±0.95 vs 1.22±0.90 in the non–BIF-CTO patients, P<.001). Procedural success was 78.9% and was not affected by the presence of bifurcation lesions (80.4% in the BIF-CTO group, 77.8% in the non–BIF-CTO-CTO group, P=.447) or the bifurcation site (proximal BIF-CTO 76.9%, mid–BIF-CTO 83.8%, distal BIF-CTO 85%, P=.204). Complication rates were similar in BIF-CTO and non–BIF-CTO.
ConclusionsThe incidence of bifurcation lesions is high in contemporary CTO PCI. Patients with BIF-CTO present with higher lesion complexity, with no impact on procedural success or complication rates when the predominant strategy is provisional stenting.
Keywords
Abbreviations
Identify yourself
Not yet a subscriber to the journal?
Purchase access to the article
By purchasing the article, the PDF of the same can be downloaded
Price: 19,34 €
Phone for incidents
Monday to Friday from 9am to 6pm (GMT+1) except for the months of July and August, which will be from 9am to 3pm