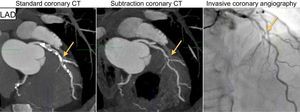
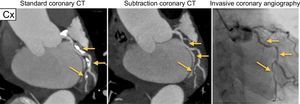
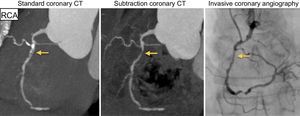
We present the case of a 65-year-old man with intermediate cardiovascular risk who presented with atypical chest pain. A noninvasive computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA) was performed, which showed severe fibrocalcific atheromatosis of the 3 main epicardial coronary vessels (calcium score of 1104 Agatston units, corresponding to the 93rd population percentile). This made interpretation of the degree of underlying stenosis difficult. However, by applying a new calcium subtraction technique, we were able to determine the presence of significant luminal stenosis in the 3 main coronary arteries: the proximal left anterior descending (LAD), the distal circumflex (Cx), and the proximal right coronary artery (RCA). The findings were subsequently confirmed with invasive coronary angiography (Figures 1–3).
Noninvasive coronary angiography is an accurate technique for the diagnosis and quantification of coronary atheromatosis; however, there is considerable scientific evidence that its diagnostic accuracy is reduced in the presence of marked coronary calcification or metallic stents with a diameter < 3 mm. Recently, calcium/metal subtraction software has been developed that allows such artefacts to be removed and greatly facilitates the interpretation of images. The technique consists of the acquisition of 2 sets of images during a single breath hold, one with iodinated contrast and another without. Subsequently, the noncontrast volume (the mask) is subtracted from the volume with contrast (standard CTCA) and the calcium/metal artefact is removed.
This new software promises to broaden the clinical applicability of cardiac CT to include patients with severe coronary artery calcification or ischemic heart disease with stent revascularization (independently of stent size).
We would like to thank Toshiba Spain for their technical support and Dr Massó for his contribution on clinical management.