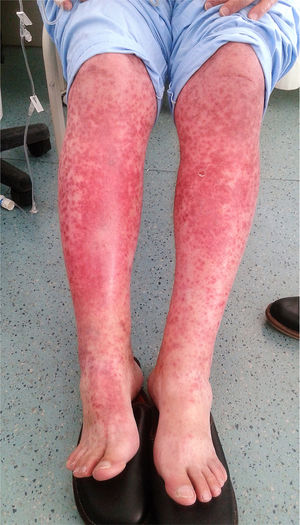
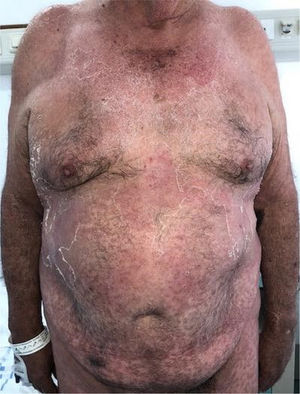
A 76-year-old man presented with an acute inferior myocardial infarct, meeting the criteria for urgent reperfusion. Following percutaneous revascularization, he was started on treatment with statins, aspirin, and clopidogrel. He progressed well and was due to be discharged early. The night before his planned discharge, after 4 days in hospital, he developed a fever and became generally unwell, with widespread cutaneous erythema spreading downwards and affecting more than 30% of the body surface area. On examination, he had confluent erythematous macules on the trunk, erythematous macules with a pseudovesicular center on the upper limbs and with a central vesical on the lower limbs, with a positive Nikolsky sign, and erosions in the areas of dressings and patches (Figure 1). A diagnosis was made of Stevens-Johnson syndrome with Severity of Illness Score for Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (SCORTEN) of 3 (probability of death, 35.5%). Clopidogrel was suspected as a likely causal agent, so his dual antiplatelet therapy was replaced with ticagrelor. With this, the erythema improved significantly, with downward-spreading desquamation, and no further temperature spikes from the second day on the new medication (Figure 2). Finally, the patient was stable from a cardiovascular perspective and was discharged for outpatient follow-up.
This case shows that, when presented with a general deterioration with fever followed by widespread cutaneous erythema in a patient recently started on clopidogrel, especially within the past month, Stevens-Johnson syndrome should be considered as a possible diagnosis, not forgetting the latent period that may occur before the clinical manifestation. The drug must be stopped due to the potentially fatal consequences of this condition in the first month.