Patients with clinically evident coronary artery disease differ in their rate of progression, which impacts prognosis. We aimed to characterize serum and genetic markers in patients with rapid clinical progression (RCP) of coronary artery disease vs those with long standing stable (LSS) disease.
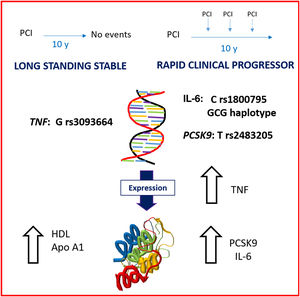
MethodsRetrospective study of cases (RCP) and controls (LSS) (1:2). Patients requiring ≥ 2 revascularizations due to atherosclerotic progression in the 10 years after a first angioplasty were considered to be RCP and those without events during the same period after the first angioplasty were considered to have LSS disease. After patient selection, we analyzed serum values, mRNA expression and genetic polymorphisms of inflammatory markers, including interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-a, and atherogenic markers consisted of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), low-density lipoprotein receptor, sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 2, and apolipoprotein-B.
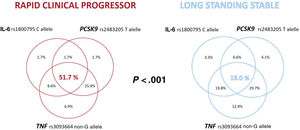
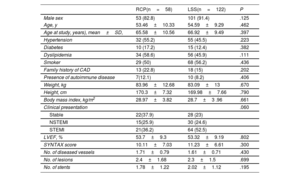
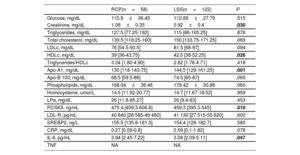
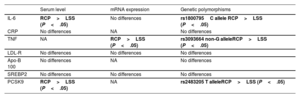
ResultsThe study included 180 patients (58 RCP and 122 LSS). Demographic characteristics, classic risk factors and the extent of coronary disease were similar in the 2 groups. Patients with RCP showed higher serum levels of interleukin-6 and PCSK9 and higher TNF mRNA expression. Interleukin-6 rs180075C, TNF rs3093664 non-G and PCSK9 rs2483205 T alleles conferred a risk of RCP (P<.05 in all cases). Among patients with RCP, 51.7% had all 3 risk alleles vs 18% of those with LSS (P<.001).
ConclusionsWe suggest the existence of specific phenotypic and genotypic markers associated with RCP of coronary artery disease that could help to individualize the type and intensity of treatment.
Keywords
Identify yourself
Not yet a subscriber to the journal?
Purchase access to the article
By purchasing the article, the PDF of the same can be downloaded
Price: 19,34 €
Phone for incidents
Monday to Friday from 9am to 6pm (GMT+1) except for the months of July and August, which will be from 9am to 3pm