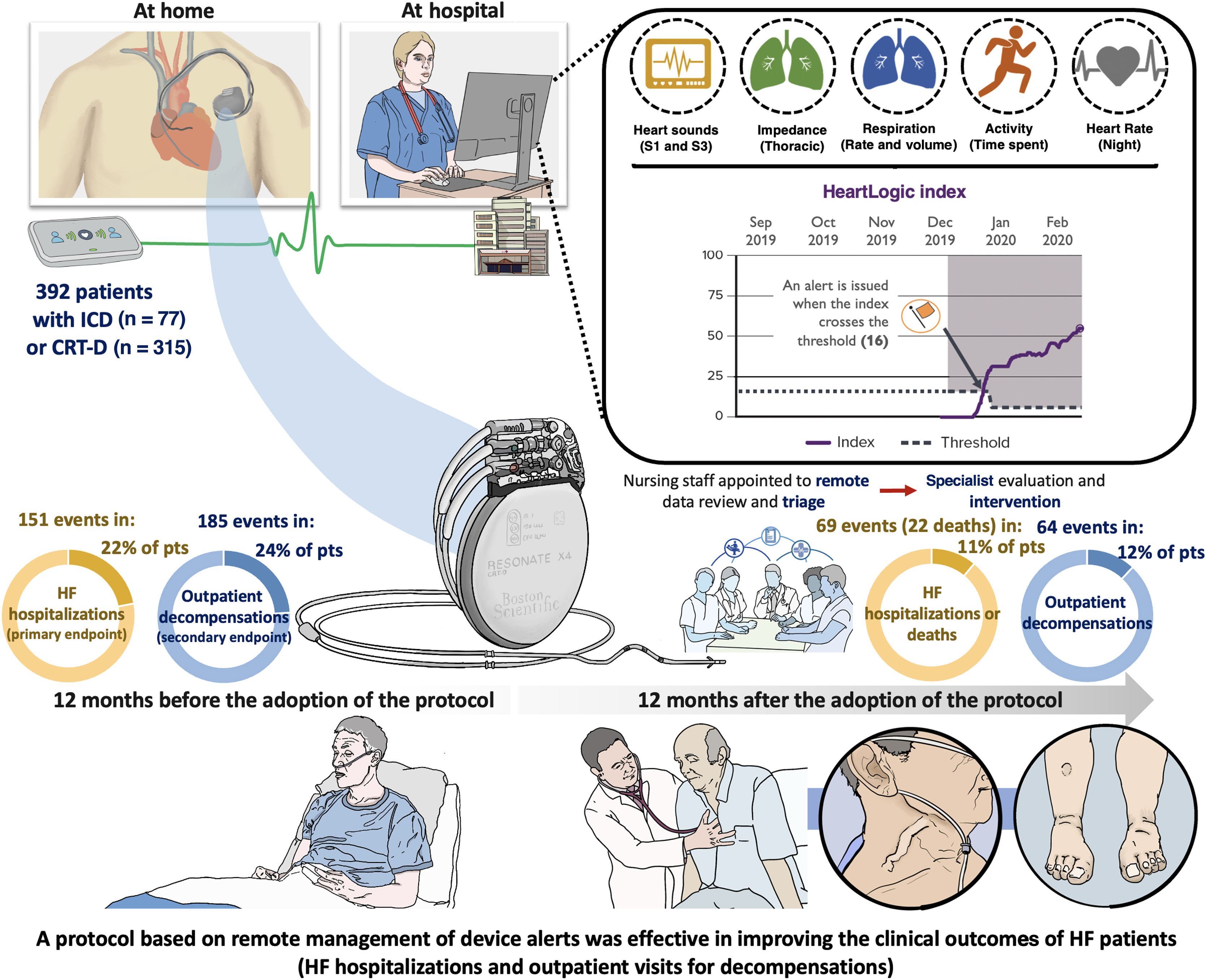
The multiparametric implantable cardioverter-defibrillator HeartLogic index has proven to be a sensitive and timely predictor of impending heart failure (HF) decompensation. We evaluated the impact of a standardized follow-up protocol implemented by nursing staff and based on remote management of alerts.
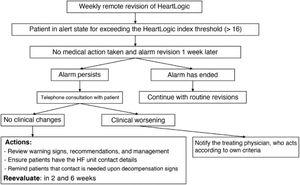
MethodsThe algorithm was activated in HF patients at 19 Spanish centers. Transmitted data were analyzed remotely, and patients were contacted by telephone if alerts were issued. Clinical actions were implemented remotely or through outpatient visits. The primary endpoint consisted of HF hospitalizations or death. Secondary endpoints were HF outpatient visits. We compared the 12-month periods before and after the adoption of the protocol.
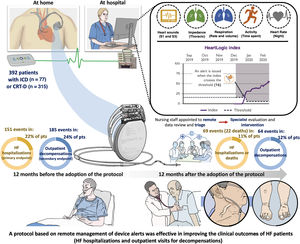
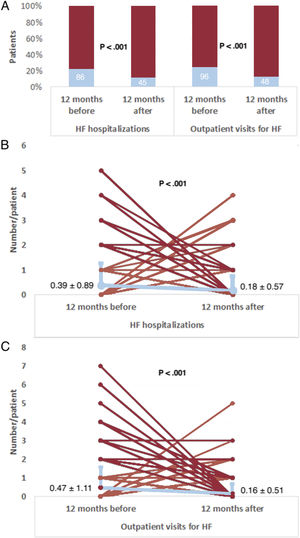
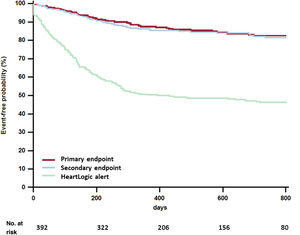
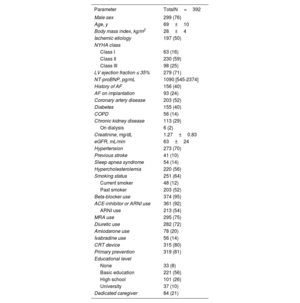
ResultsWe analyzed 392 patients (aged 69±10 years, 76% male, 50% ischemic cardiomyopathy) with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (20%) or cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillators (80%). The primary endpoint occurred 151 times in 86 (22%) patients during the 12 months before the adoption of the protocol, and 69 times in 45 (11%) patients (P<.001) during the 12 months after its adoption. The mean number of hospitalizations per patient was 0.39±0.89 pre- and 0.18±0.57 postadoption (P<.001). There were 185 outpatient visits for HF in 96 (24%) patients before adoption and 64 in 48 (12%) patients after adoption (P<.001). The mean number of visits per patient was 0.47±1.11 pre- and 0.16±0.51 postadoption (P<.001).
ConclusionsA standardized follow-up protocol based on remote management of HeartLogic alerts enabled effective remote management of HF patients. After its adoption, we observed a significant reduction in HF hospitalizations and outpatient visits.
Keywords
Identify yourself
Not yet a subscriber to the journal?
Purchase access to the article
By purchasing the article, the PDF of the same can be downloaded
Price: 19,34 €
Phone for incidents
Monday to Friday from 9am to 6pm (GMT+1) except for the months of July and August, which will be from 9am to 3pm